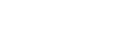“Viva Grass Planner” for Protected areas
Protected areas DMS story
Currently, most protected area administrations (PAA) lack a full view on how much valuable grasslands (and/or other habitat types) they have and what is its management status. Many PAA organize the management of grasslands looking only at few indicators such as habitats of EU importance, but more holistic and analytical view at all grasslands in the area is lacking. E.g. such as statistical information of how many grasslands (ha) are covering protected area, what share is regularly maintained, how many needs restoration, how many is declared under agri-env. measures, etc.
Decision making process of PAA’s on which grasslands should be managed firstly is often happening very subjectively – areas, which are more known or promoted by specialists of PAA are given priority, but they are not necessarily the most important due to the management urgency, occurrence of protected species or similar criteria looking both, at the protected area level and national level. This is an important issue to deal with as protected areas have limited financial and human resources, as well as the whole national environmental sector, therefore resources in the first place should be allocated to the priority areas according to many indicators.
The role of Viva Grass Planner in this DMS
To this DMS related stakeholders:
- Administrations of protected areas (PA administration)
- Ministry of Environment
Viva Grass Planner functionality important for this DMS:
-
- Org. account. Every organization gets their own part of the cloud based system. This part can be managed and customized by organization’s administrator/user and adopted to the their needs. Organization can have and manage different territory. It can be whole country, municipality, protected area or even farm. Organization’s data is not available for other Planner users in any form.
- Data from basemap + VG context data layers. During the Viva Grass project a lot of methodologies and data sets were developed. Some dataset structure and prepared data can be re-used by organization to speed organization’s Viva Grass Planner account preparation and to be able to start data assessment or other spatial data based decision making faster.
Context data layers provided by Viva Grass lets organization to have important spatial context without need to search for the available data, without integration to the Tool, etc. - Org.’s context data layers. It is a list of identified and pre-configured context data layers. Every organization can use this structure to upload or tu enter their own contextual data and to use it for the calculations (intersection), context data storage and management. More when 10 thematic layers and their structures are provided. Three additional custom context data layers for a point, line and polygon features are available too. These custom layers can be used to upload and use for any type of context data.
- Custom attributes. For the different needs of every organization it is possible to add custom attributes to the land use block polygons. The formats or the attributes can be text, double, integer. Attributes can be used to store temporary or permanent information about land use blocks, can be used to store calculation, prioritization results, etc.
- Functionality:
-
-
- Visual analysis/assessment. Viva Grass Planner provide weight range of map functionality: basemap selector, 3rd party data upload, zoom in/zoom out, location search, map layer management including possibility to change layer transparency, etc. All this lets assess map data visually and to make spatial data based decisions.
-
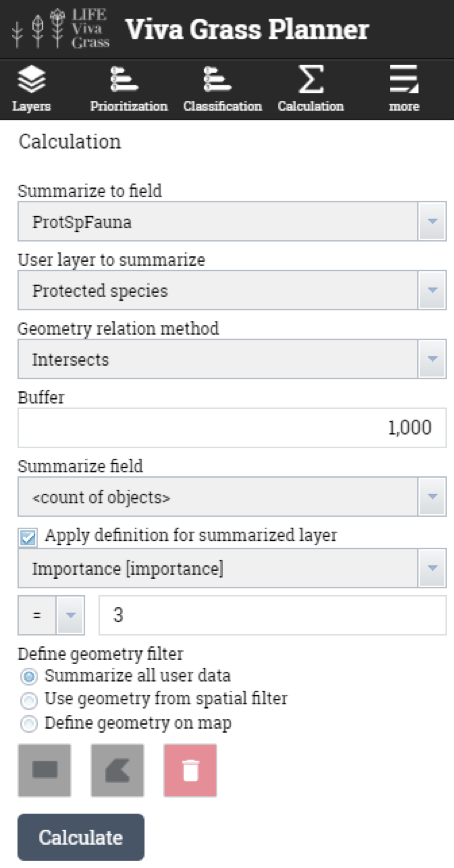
- Calculation. It is one of the most powerful tools in Viva Grass Planner. This simple to use tool lets intersect land use blocks with a selected context data layer and to store this intersection result as a attribute info in the land use block.
- Classification. This functionality lets to classify land use blocks to different categories based on advanced selection expressions related to the land use block attribute information.
- Prioritization. This functionality enables the user to prioritise his land use blocks according to the selected attributes from the land use block attribute information by giving these attributes a certain weight.
- Upload/Download. This is very important functionality of the Tool, because you can download data you need in any step, you can modify it in other (ex. ArcGIS for Desktop) tools and upload back to the Viva Grass Planner Tool.
Adding context data layers
Viva Grass Planner >> more >> Settings >> Layers settings
A wide range of prepared contextual layers are provided within the Tool in this DMS. The data in the layers can be added in the Tool itself using certain functionality or prepared outside the Tool on desktop applications (e.g. ArcGIS for Desktop) and then uploaded to the Tool.
Turn on layers listed below by checking checkboxes.
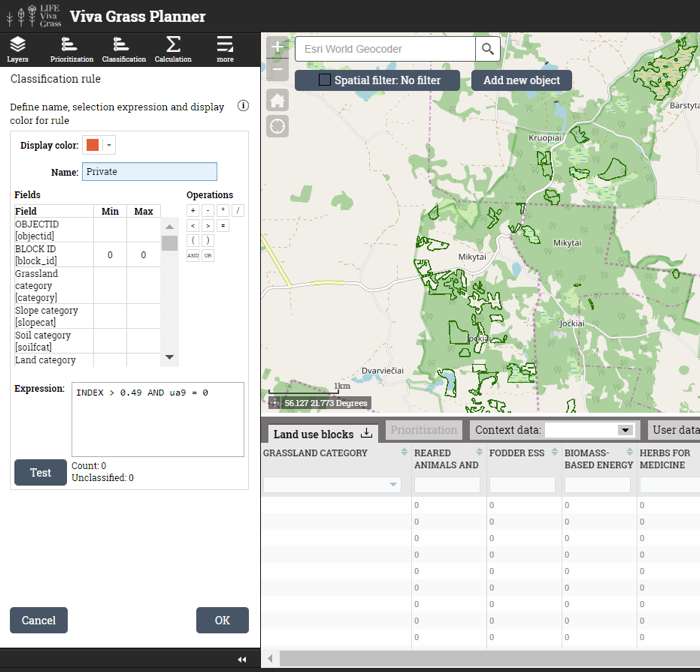
Context data layer list:
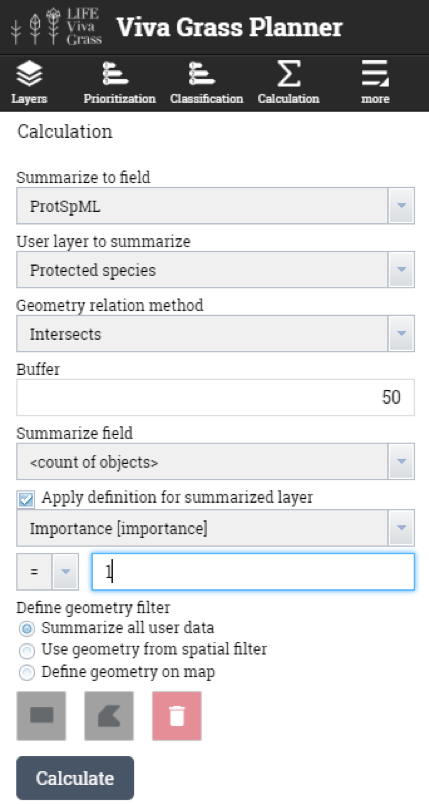
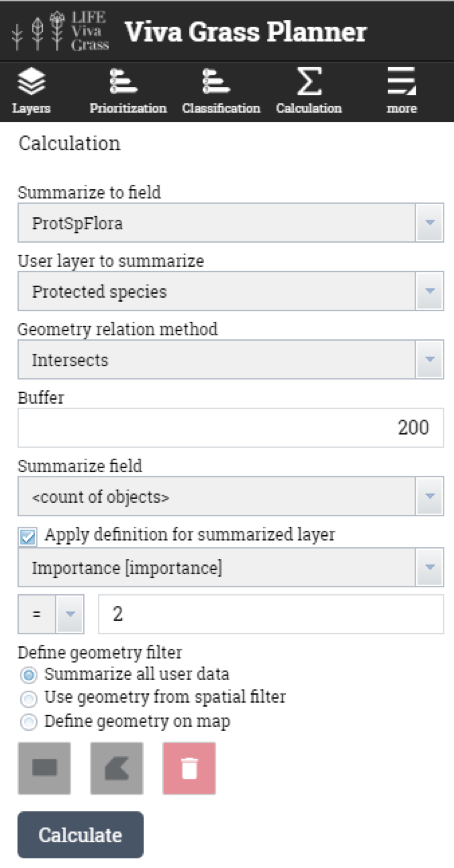
- Protected species (points) – will be used to intersect (with 50 m (lichens and mushrooms), 200 m (flora), 1000 m (fauna) buffer) with land use blocks to calculate the number of protected species that are within the buffer zone of the grassland.
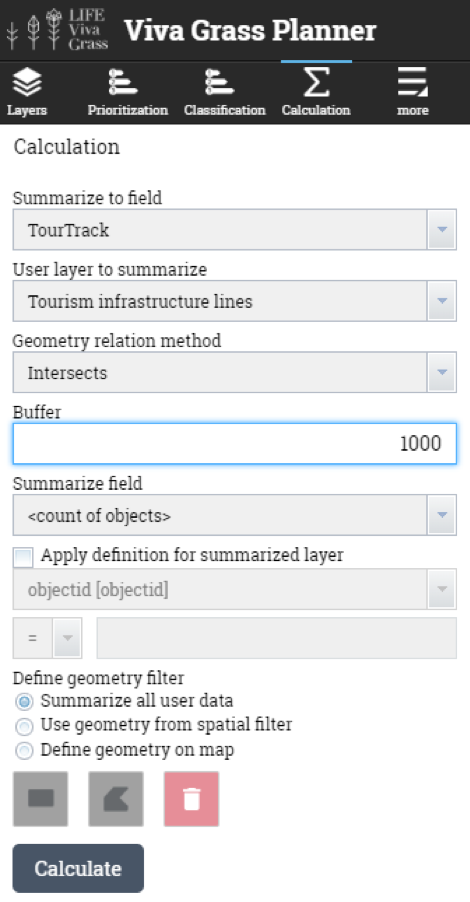
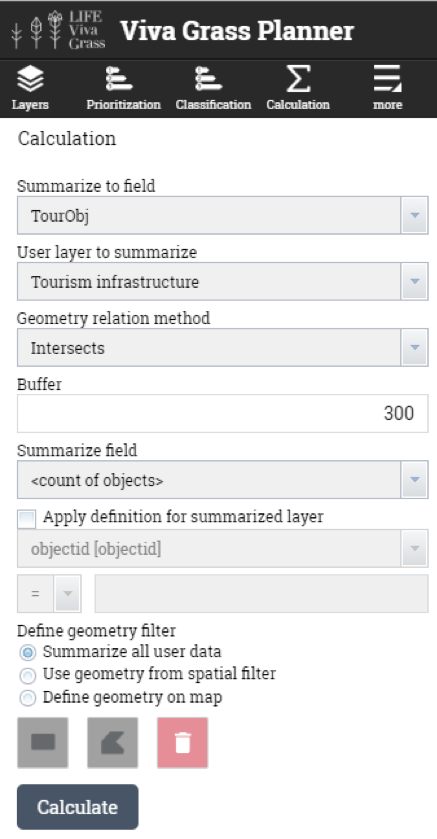
- Tourism infrastructure (points) – will be used to intersect (with 300 m buffer) with land use blocks to calculate the number of tourism infrastructure objects that are within the buffer zone of the grassland.
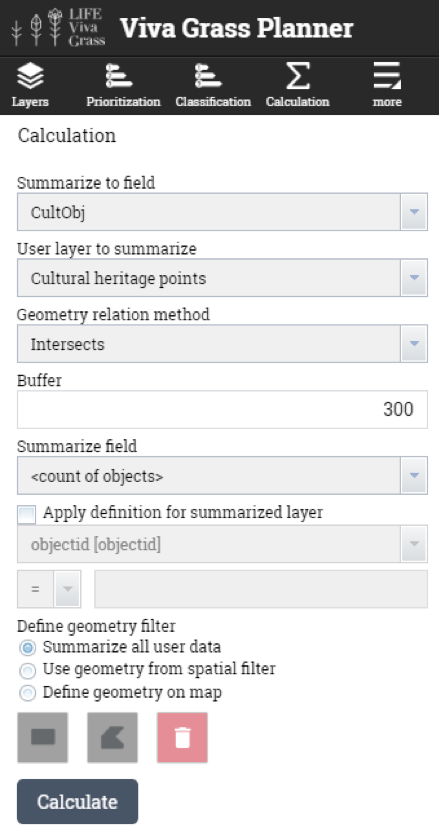
- Cultural heritage (points) – will be used to intersect (with 300 m buffer) with land use blocks to calculate the number of cultural heritage objects that are within the buffer zone of the grassland.
- Nature objects (points) – will be used to intersect (with 300 m buffer) with land use blocks to calculate the number of nature heritage objects that are within the buffer zone of the grassland.
- Tourism infrastructure (lines) – will be used to intersect (with 1000 m buffer) with land use blocks to highlight the ones that have a tourist route or track passing their buffer.
- Habitats (polygon) – will be used to intersect with land use blocks, to know which of them have are within a EU habitat, are within a priority EU habitat or are not within a EU habitat.
- Rivers (lines) – will be used as a contextual data layer for visualisation.
- Roads (lines) – will be used as a contextual data layer for visualisation.
Other context layers can be switched on or off if needed.
Important! To see changes user needs to reload Tool and login once again.
Adding custom attributes
Viva Grass Planner >> More >> Settings >> User attributes
Add additional, custom attributes for the Land use blocks. These attributes can be used to store additional data about land use blocks, to store calculation, intersection, classification or prioritization results, etc.

| ua1 | Habitat | Double |
| ua2 | TourTrack | Double |
| ua3 | CultObj | Double |
| ua4 | NatObj | Double |
| ua5 | TourObj | Double |
| ua6 | ProtSpML | Double |
| ua7 | ProtSpFlora | Double |
| ua8 | ProtSpFauna | Double |
| ua9 | LandOwn | Double |
For this case we will need:
- Habitat (Double) – to store info if land use block intersects with a EU habitat (1), intersects with a EU priority habitat (2), does not intersect with a habitat at all (0)
- TourTrack (Double) – to store an attribute if the land use block (1000 m buffer) is intersected by a touristic track or trail
- CultObj (Double) – to calculate the amount of cultural heritage objects that fall within the land use block (300 m buffer)
- NatObj (Double) – to calculate the amount of nature heritage objects that fall within the land use block (300 m buffer)
- TourObj (Double) – to calculate the amount of tourism objects that fall within the land use block (300 m buffer)
- ProtSpML (Double) – to calculate the amount of protected species (mushrooms and lichens) that fall within the land use block (50 m buffer)
- ProtSpFlora (Double) – to calculate the amount of protected species (flora) that fall within the land use block (200 m buffer)
- ProtSpFauna (Double) – to calculate the amount of protected species (fauna) that fall within the land use block (1000 m buffer)
- LandOwn (Double) – to store information if the land use block is of private ownership (0) or state owned (1)
Other attributes can be added if needed.
Important! To see changes user needs to reload Tool and login once again.
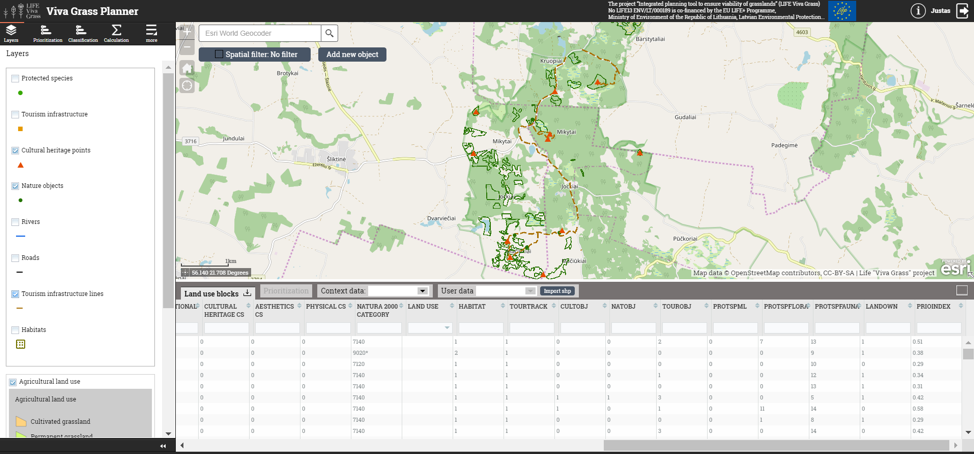
Additional attribute calculation
Viva Grass >> Calculation
Attribute calculation can be done in ArcGIS for Desktop or in the “Viva Grass Planner”. This tool lets intersect two layers (land use blocks and selected org’s contextual layer), intersect with a defined buffer (around land use block), find land use blocks which are within org’s contextual data layer polygons and how much elements from org’s context data layer land use block contains.
Land use blocks which are within EU habitat, priority EU habitat or not within EU habitats
In this step land use blocks which intersects with habitat polygons (org’s context data layer “Habitat”). As the result we get a list of land use blocks in EU habitat polygons.
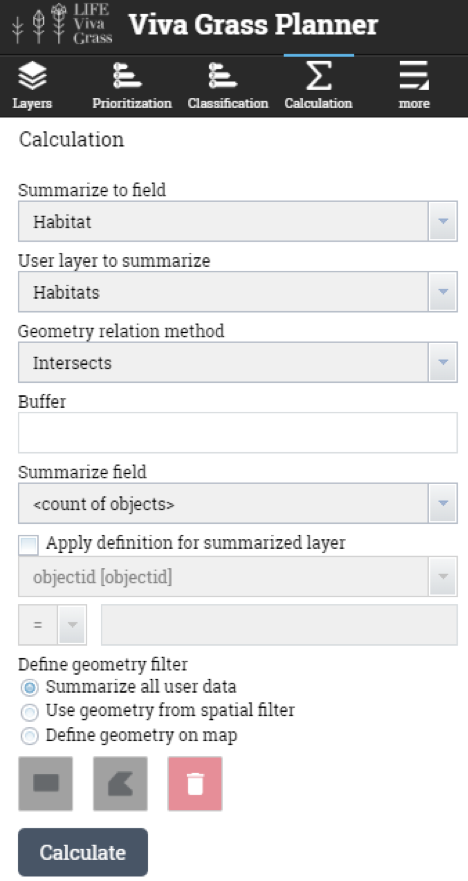
“Habitat” > 0 means land use block is in EU habitat.
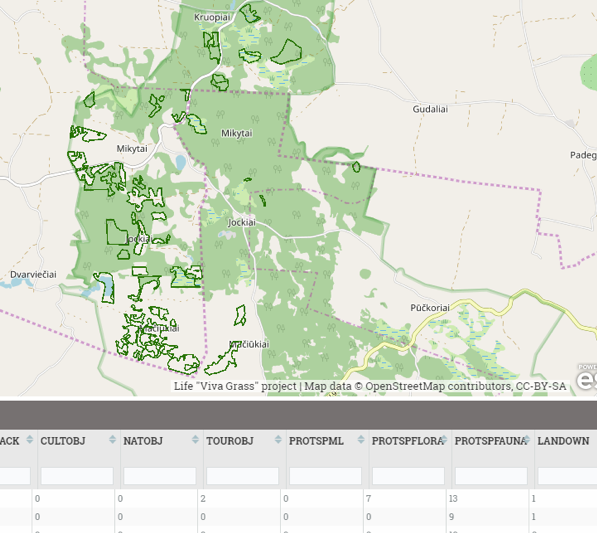
Calculation results can be checked by filtering attribute table data (Habitat > 0):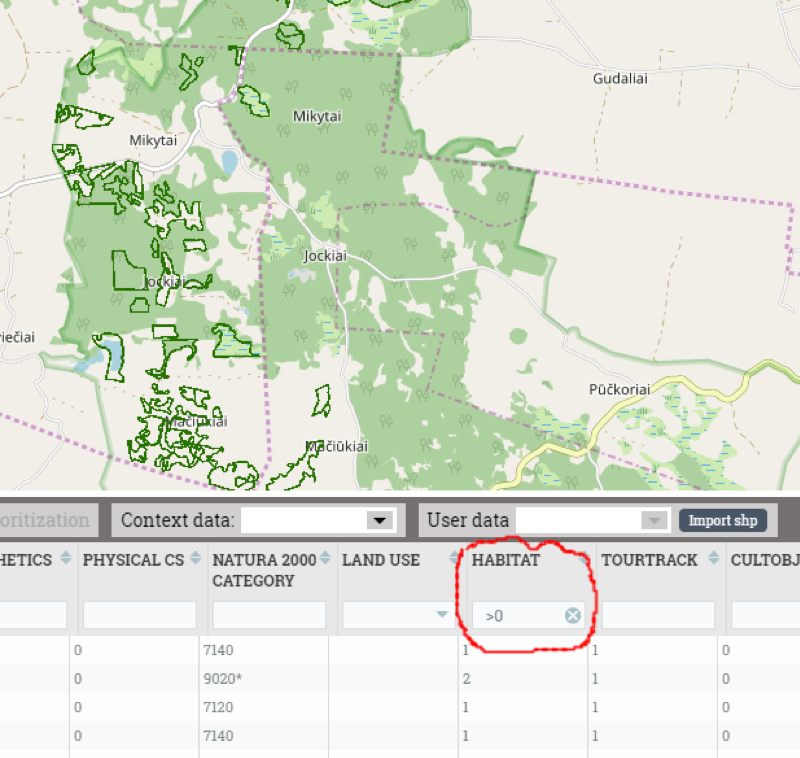
- Land use blocks close to tourism routes (1000 m. buffer)
- Land use blocks having cultural objects or are close to them (300 m.)
- Land use blocks having nature objects or are close to them (300 m.)
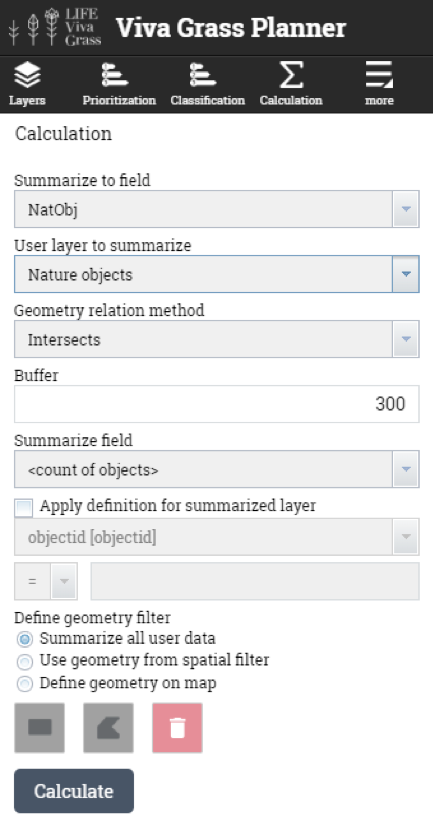
- Land use blocks having tourism objects or are close to them (300 m.)
- Land use blocks having lichens and mushrooms or are close to them (50 m.)
- Land use blocks having flora species or are close to them (200 m.)
- Land use blocks having fauna species or are close to them (1000 m.)
This functionality enables the user to prioritise his land use blocks according to the selected attributes from the land use block attribute information by giving these attributes a certain weight.
Important! Topic related attributes are calculated and stored into the structure of the Viva Grass Planner database. Now these values, together with other land use block attributes, such as land use type, land use, land quality, slope, ES values, bundles, trade-offs, etc. can be used for classification, prioritization and visual analysis.
Prioritization of management plots
Having many management plots and limited resources the PAA’s have to decide which plots should receive priority and be restored or managed first. This can be done subjectively or by using data collected in the fields and from other data sources. This way connecting the data to certain attributes and giving them certain weights, a more precise selection of the priorities can be made. Before starting the prioritization process, the user of the Tool can decide which plots should be prioritized.
In this demo case we will be prioritizing all the plots, which need restoration activities to be implemented. In the prioritization we will be giving the most attention to conserving the most valuable habitats and protected species.
Demo steps:
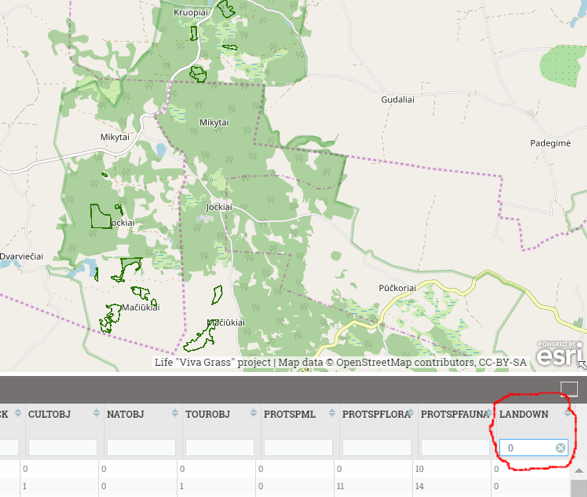
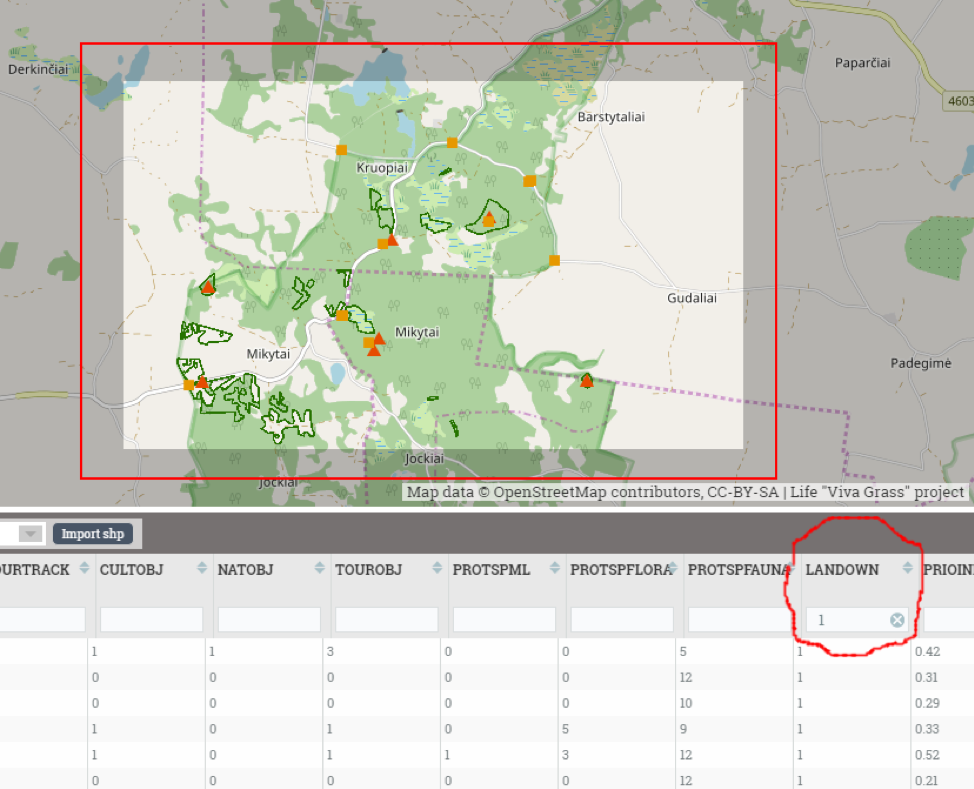
- Filter land use blocks of interest (Attribute filtering example. “LandOwn = 0” (private owners) or “LandOwn = 1” (land owned by government))
All territories:
Filtered by attribute (“LandOwn” = 0 (private land))
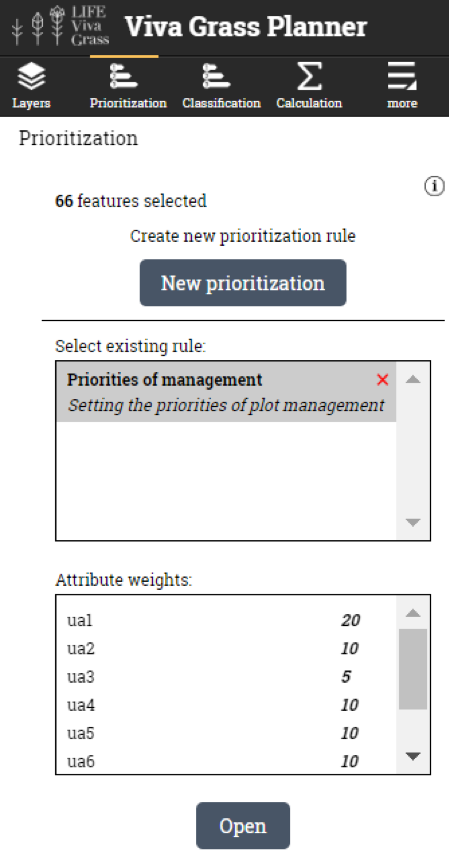
- Open prioritization Tool (Viva Grass Planner >> Prioritization)
- You can create a new prioritization rule by pressing “New prioritization” button or use and existing saved rule if you have one by selecting it from the “Select existing rule:” panel and pressing “Open”.
- Opening prioritization rule
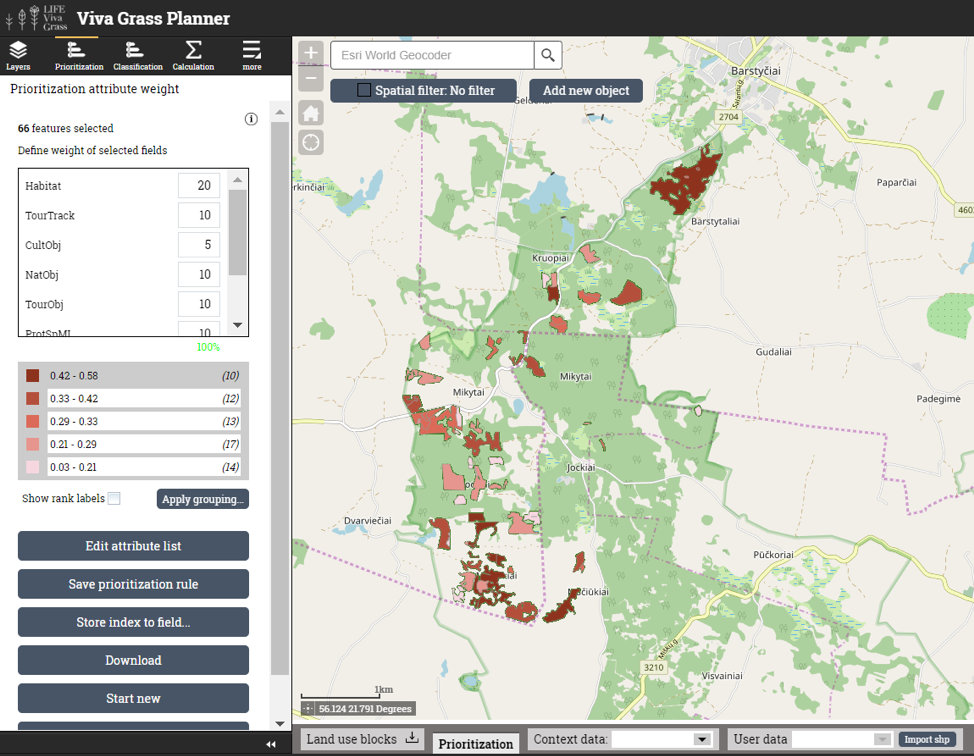
- Editing prioritization rule. You can edit the prioritization rule. This can be done by selecting new attributes for the prioritization and changing their weights.
- Change attribute list (“Edit attribute list”)

- Change weights
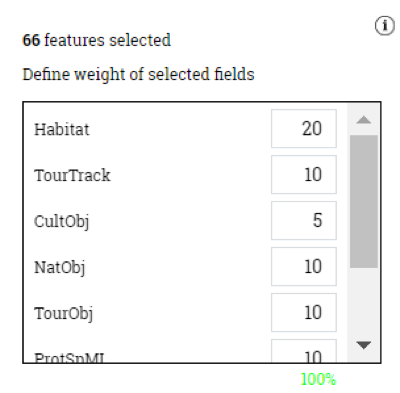
- Save as a new rule
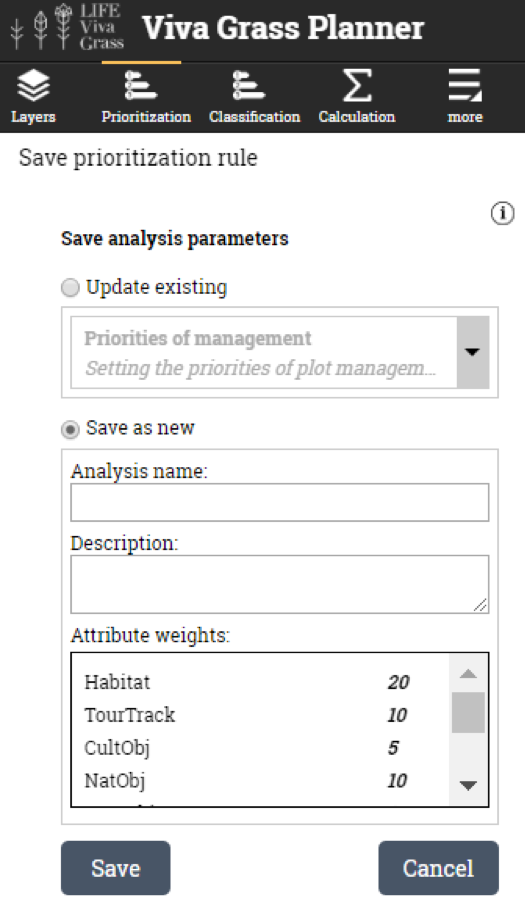
-
- Update existing
- Save as new
-
- Priority index value visualization
- Change attribute list (“Edit attribute list”)
- Prioritization result appears in map layer list
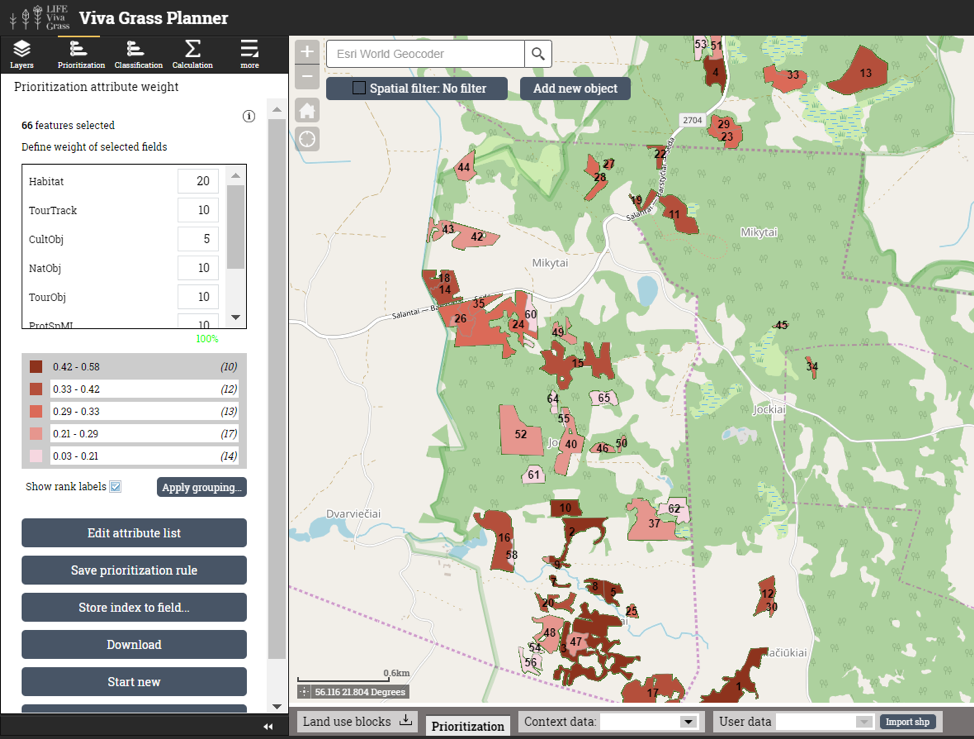
Prioritization attributes and weights:
| Attribute | Weight | Comments |
| Habitat | 35 % | Good status managed habitats are the foundation for all the species to thrive, therefore we give the most attention to plots where the EU importance habitats area. The priority EU habitats get an extra score. |
| ProtSpML | 10 % | Protected species (mushrooms and lichens) are relatively settled species, therefore we give them the least weight, as they are not our primary attention object, though they are still important to be considered. |
| ProtSpFlora | 30 % | Conserving the existing protected species (flora) and enhancing the spread of new individs is very important for us, therefore this indicator gets the second highest weight. |
| ProtSpFauna | 25 % | Conserving the existing protected species (fauna) is very important for us as well as stimulating the growth of the populations, which are connected to good habitat quality and certain species also, therefore this indicator gets a smaller weight but still is significantly important. |
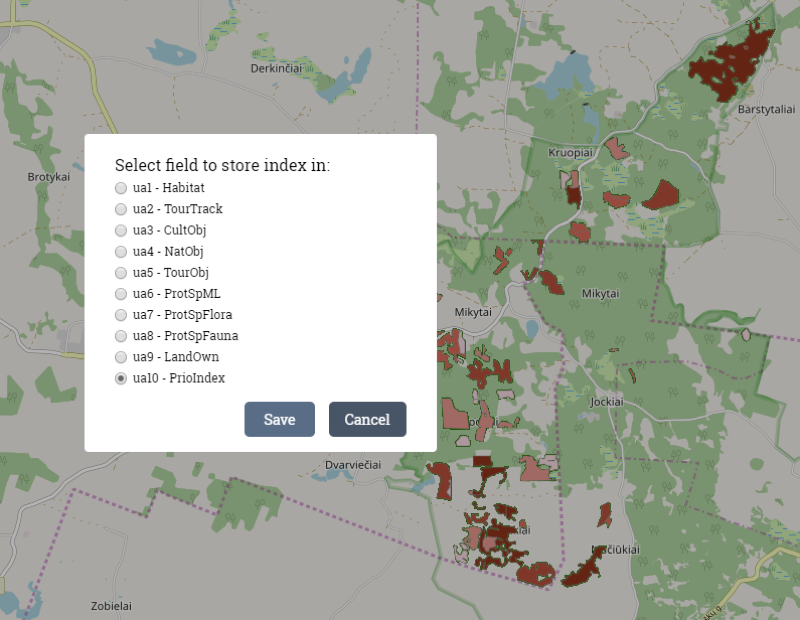
- Store index to field (PrioIndex). For this reason additional custom attribute was created. Stored index values can be used in other Tool functionalities – classification, shown in pop-up or edited.
Classification of the highest priority land use blocks
Having the prioritization results we can still work forward with the Tool and apply the classification functionality. In this case it is important for the PAA to see which of the highest priority land use blocks belong to the private owners and which to the state. Knowing this information further steps can be taken in seeking the restoration of the grassland plots. Private landowners can be found and asked to restore their lands or at least contribute to the restoration. While state owned land would be restored from state money by the PAA itself, later promoting the restored grasslands to local farmers for the long run management.
Demo steps:
- All land use blocks or filtered by attribute and spatially can be classified. For this DMS we will use all blocks.
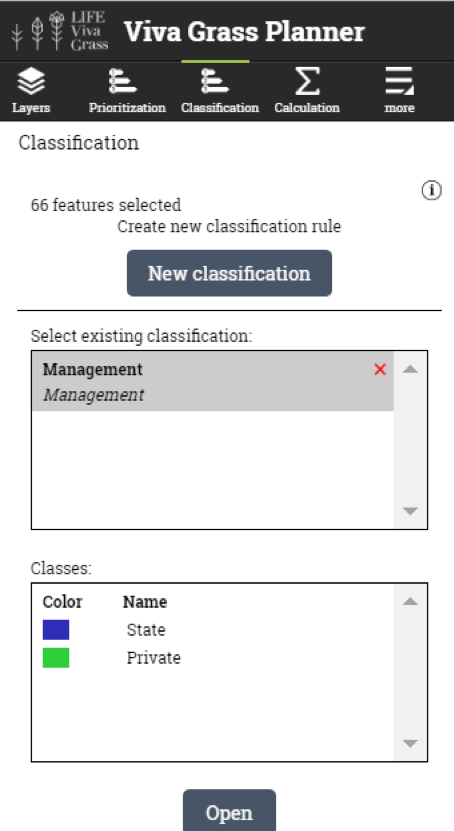
- Open classification Tool (Viva Grass Planner >> classification)
- You can create a new classification rule by pressing “New classification” button or use and existing saved rule if you have one by selecting it from the “Select existing classification:” panel and pressing “Open”.
- Opening classification

- Editing or creating classes. You can edit the existing or create new classes within the rule. This is done by manually writing the expression and validating it by pressing the “Test” button.

- Classification result appears in map layer list
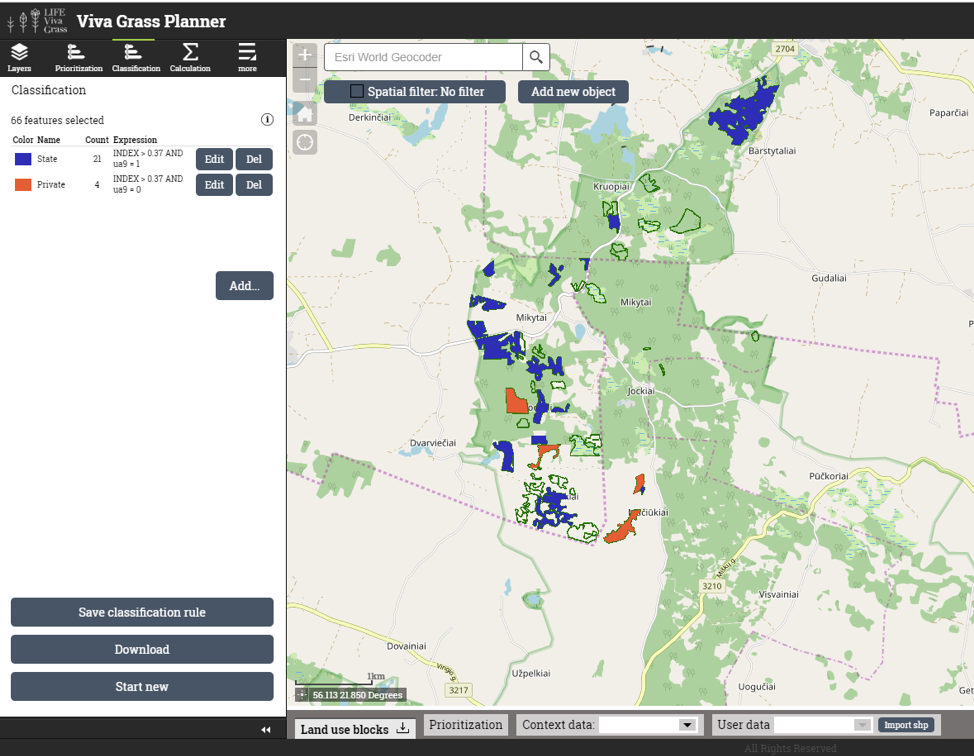
Classification rules (stored in classification rule “Management”):
| Class name | Expression | Recommended approach |
| State | INDEX > 0.37 AND ua9 = 1 | Restore grasslands with state money and promote the restored grasslands to local farmers for long term management |
| Private | INDEX > 0.37 AND ua9 = 0 | Encourage private owners to restore their lands or contribute to the restoration and long term management |
Defining the important grasslands to be managed in the long perspective
As we have prioritized the plots to be restored in the previous scenario, now PAA’s mission is to seek for the long-term management of the restored areas. The PAA is also planning not only to ensure long-term management of the restored areas, but also open them to the public by planning tourist paths and trails and other touristic objects and infrastructure. Therefore in this scenario we will prioritize the grasslands not only according to natural values, but also to the planned infrastructure, which is meant for the people to come to the area and acknowledge the ecosystem services these grasslands provide and the values they hold.
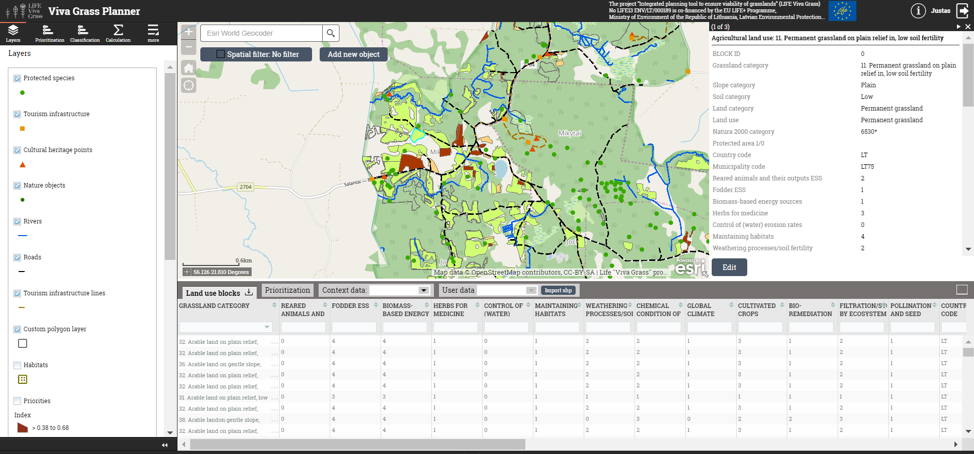
Demo steps:
The prioritization steps in this scenario are similar to the ones above in the first scenario, however here we use additional attributes to get a more holistic and comprehensive view of the situation.
| Attribute | Weight | Comments |
| Habitat | 15 % | Good status managed habitats are the foundation for all the species to thrive, therefore we give it high weight. These will be also interesting for the tourists to explore. |
| TourTrack | 15 % | One of the objectives of the prioritization is to have the grasslands near the planned tourist trails to be in good status, therefore this indicator also receives a high weight. |
| CultObj | 10 % | Cultural heritage objects will be interesting for tourists to see, therefore the grasslands where they are situated should also be in good status. |
| NatObj | 10 % | Nature heritage objects will be interesting for tourists to see, therefore the grasslands where they are situated should also be in good status. |
| TourObj | 15 % | One of the objectives of the prioritization is to have the grasslands near the planned tourist objects to be in good status, therefore this indicator also receives a high weight. |
| ProtSpML | 5 % | Protected species (mushrooms and lichens) are quite vulnerable therefore we don’t want them to be to exposed to tourists, however grasslands where they are situated are still important. |
| ProtSpFlora | 15 % | Protected species (flora) will be one of the things for the tourists to see and learn about therefore it is important to have the grasslands where they are located to be in good status. |
| ProtSpFauna | 15 % | Nevertheless that we want to show the ecosystem services that the grasslands provide to the public, it is also important to keep the the good shape of grasslands where the Protected species (fauna) are found. |
Prioritization results:
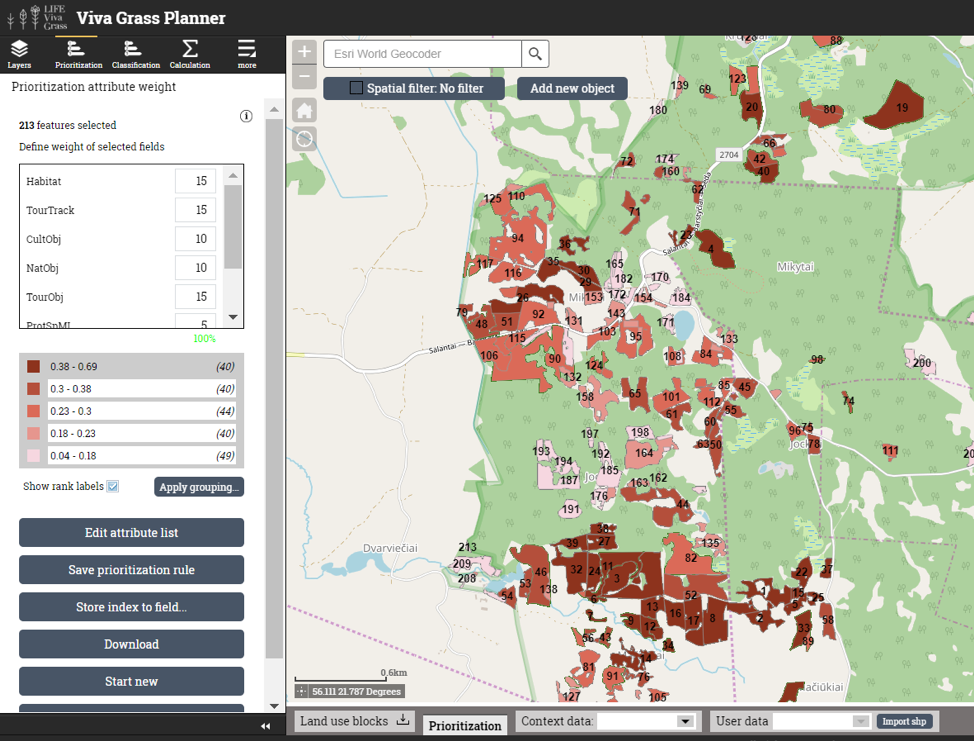
Prioritization results are shown in the map and can be used with other map layers: organization’s land use blocks, context data layers or even with “LIFE Viva Grass” contextual layers.
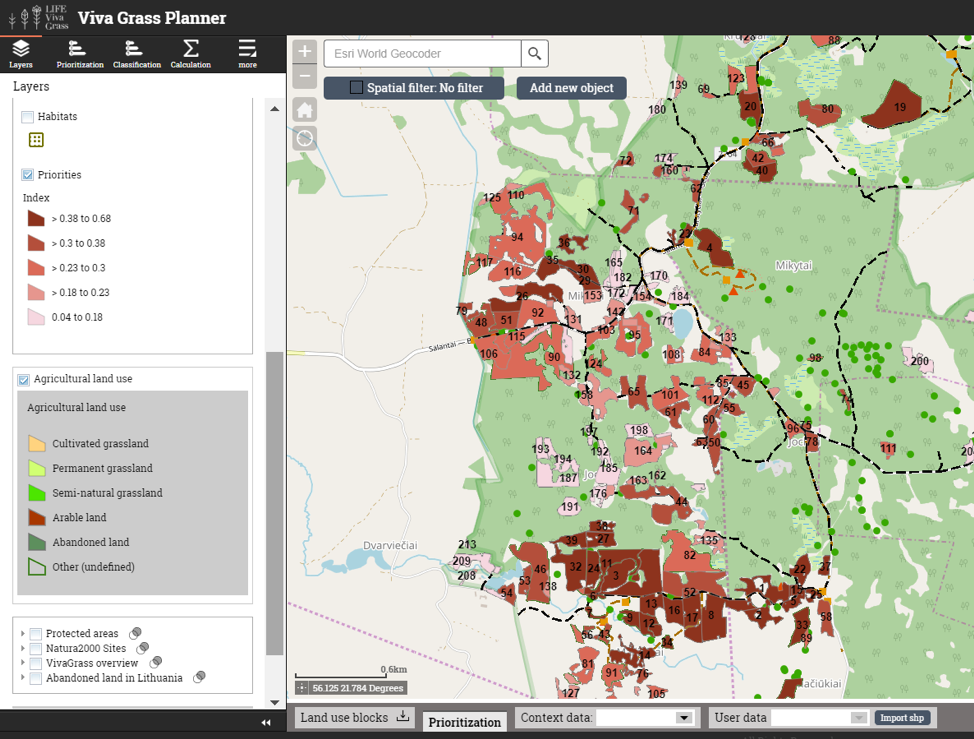
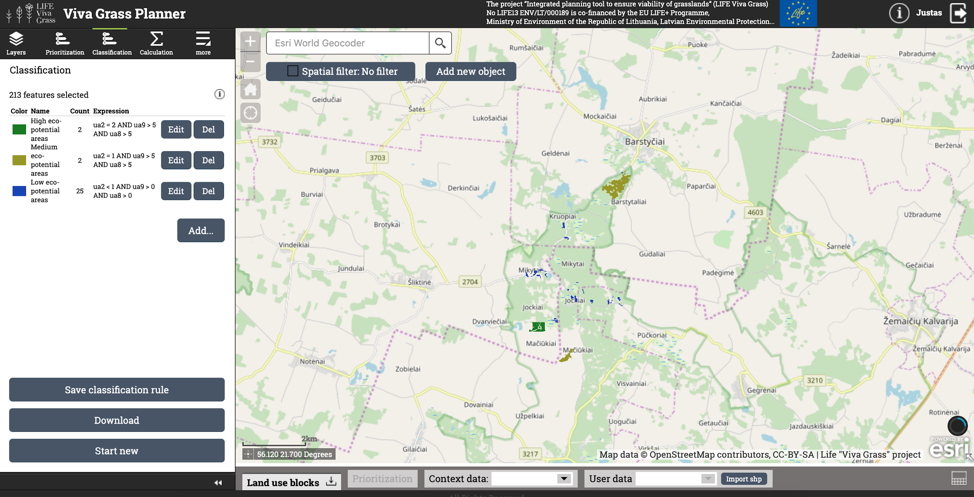
Classification of grasslands
The data can be analyzed differently in another approach. Instead of prioritizing the grasslands in a weighted manner, you can use the classification functionality to get different results by using raw data values and combining them in different ways.
A simple example is given below (stored in classification rule “Eco-potential of areas”):
| Class name | Expression | Explanation |
| High eco-potential areas | ua2 = 2 AND ua9 > 5 AND ua8 > 5 | Plots, where EU priority habitat (ua2 = 2) is present and more than 5 species of fauna (ua9) and flora (ua8) are found |
| Medium eco-potential areas | ua2 = 1 AND ua9 > 5 AND ua8 > 5 | Plots, where EU habitat (ua2 = 1) is present and more than 5 species of fauna (ua9) and flora (ua8) are found |
| Low eco-potential areas | ua2 < 1 AND ua9 > 0 AND ua8 > 0 | Plots, where EU habitat (ua2 = 0) is not present and more than 0 species of fauna (ua9) and flora (ua8) are found |