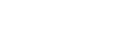Green infrastructure (GI) DMS scenario
Green Infrastructure DMS story
In the lowland landscapes of intensive agriculture practices with dense river network runoff pollution (diffuse contamination of streams with nutrients, chemicals and organic matter) is serious problem. Creating buffer zones of semi-natural vegetation around streams is well documented effective practice to mitigate negative effects of industrial agriculture and lower levels of eutrophication in both inland waters and sea. Green Infrastructure (GI) is intentionally planned natural or semi-natural ecosystems serving to mitigate human induced environmental hazards. In the context of this DMS we define GI as agro-ecosystems providing wide range of services, and especially regulating services, and especially connected with nutrient cycling (filtration/accumulation/storage and chemical conditions of freshwaters). Viva Grass ES assessment matrix reveals that both permanent and semi-natural grasslands provide above average values in those groups of ES. As a case study area for testing this DMS we have chosen basin of river Lielupe, the reason for this is twofold – it is most intensive industrial agricultural region in Baltics with high levels of diffuse pollution (connected with agricultural nutrient runoff); it is cross border region where problems is harder to grasp and address in national level.
The role of Viva Grass Planner in this DMS
To this DMS related stakeholders:
- Agriculture land-use planners
- Agro-ecologists – research institutions
- Environmental protection planners
- Policy-makers in agriculture and environmental protection
- Municipalities
Viva Grass Planner functionality important for this DMS:
-
- Org. account. Every organization gets their own part of the cloud based system. This part can be managed and customized by organization’s administrator/user and adopted to the their needs. Organization can have and manage different territory. It can be whole country, municipality, protected area or even farm. Organization’s data is not available for other Planner users in any form.
- Data from basemap + VG context data layers. During the Viva Grass project a lot of methodologies and data sets were developed. Some dataset structure and prepared data can be re-used by organization to speed organization’s Viva Grass Planner account preparation and to be able to start data assessment or other spatial data based decision making faster.
Context data layers provided by Viva Grass lets organization to have important spatial context without need to search for the available data, without integration to the Tool, etc. - Org.’s context data layers. It is a list of identified and pre-configured context data layers. Every organization can use this structure to upload or tu enter their own contextual data and to use it for the calculations (intersection), context data storage and management. More when 10 thematic layers and their structures are provided. Three additional custom context data layers for a point, line and polygon features are available too. These custom layers can be used to upload and use for any type of context data.
- Custom attributes. For the different needs of every organization it is possible to add custom attributes to the land use block polygons. The formats or the attributes can be text, double, integer. Attributes can be used to store temporary or permanent information about land use blocks, can be used to store calculation, prioritization results, etc.
-
- Functionality:
- Visual analysis/assessment. Viva Grass Planner provides a wide range of map functionality: basemap selector, 3rd party data upload, zoom in/zoom out, location search, map layer management including possibility to change layer transparency, data filter by attribute values, etc. All this lets assess map data visually and to make spatial data based decisions.
- Functionality:
- Calculation. It is one of the most powerful tools in Viva Grass Planner. This simple to use tool lets intersect land use blocks with a selected context data layer and to store this intersection result as a attribute info in the land use block. For this DMS it is used to select land use blocks which are close to riverbeds, are in flood risk zones, etc.
- Classification. This functionality lets to classify land use blocks to different categories based on advanced selection expressions related to the land use block attribute information. For this DMS it will be used to classify land use blocks into a land blocks which already acts as a Green Infrastructure and to find and show potential arable and cultivated grassland plots to turn into permanent grassland to function as GI.
- Upload/Download. This is very important functionality of the Tool, because you can download data you need in any step, you can modify it in other (ex. ArcGIS for Desktop) tools and upload back to the Viva Grass Planner Tool.
Adding context data layers
Viva Grass Planner >> More >> Settings >> Layers settings
Turn on layers listed below by checking checkboxes.

Context data layer list:
- Rivers (lines) – will be used to intersect (with 50 m buffer) with land use blocks to get land use blocks which are close to the riverbeds.
- Custom Polygon Layer (polygons) – Flood risk zones – will be used to intersect with land use blocks to get land use blocks which are (or intersects with) in flood risk zones.
Other context layers can be switched on or off if needed.
Important! To see changes user needs to reload Tool and login once again.
Adding custom attributes
Viva Grass Planner >> More >> Settings >> User attributes
Add additional, custom attributes for the Land use blocks. These attributes can be used to store additional data about land use blocks, to store calculation, intersection, classification or prioritization results, etc.

| ua1 | NearRiver | Double |
| ua2 | InFlood | Double |
For this case we will need:
- NearRiver (Double) – attribute to store info if land use block is close to river (50 m buffer)
- InFlood (Double) – attribute to store info if land use block is in the flood risk zone.
Other attributes can be added if needed.
Important! To see changes user needs to reload Tool and login once again.
Additional attribute calculation
Viva Grass >> Calculation
Attribute calculation can be done in ArcGIS for Desktop or in the Planner. This tool lets intersect two layers (land use blocks and selected org’s contextual layer), intersect with a defined buffer (around land use block), find land use blocks which are within org’s contextual data layer polygons and how much elements from org’s context data layer land use block contains.
- Land use blocks near the rivers
In this step land use blocks which are close to the rivers (50 m. buffer) are identified.

“ > 0 ” means land use block is close to the river (50 m.).
Calculation results can be checked by filtering attribute table data (NearRiver > 0):

- Land use blocks in flood risk zones

Calculation results can be checked by filtering attribute table data (InFlood > 0):

Important! GI related attributes are calculated and stored into the structure of the Viva Grass Planner database. Now these values, together with other land use block attributes, such as land use type, land use, land quality, slope, ES values, bundles, trade-offs, etc. can be used for classification, prioritization and visual analysis.
Classification of priority to create GI
The task is to classify farmland fields of intensive agriculture practices (arable land and cultivated grassland) according to their priority to be used as elements of GI via land use change to permanent grassland. Priority rule is based on the set of agro-ecological conditions and geographical position (to the flood zones and river network) of each field inside territory of analysis. The highest priority is assigned to the fields were both agro-ecological conditions (soil composition – organic) and position in landscape (close to rivers and inside flood zone) is detected. Not only runoff from fields with organic soils is more contaminated with organic matter, but also their ploughing is harmful to climate via carbon emissions. Second highest priority is assigned to the fields in the same geographical position, but on mineral soils as hazard from runoff do not contain as much organic matter, but their position inside flood zone signifies possibility that spring floods could highly intensify removal of nutrients and degrade the soil. Following priorities are assigned according to levels of lowering risks and possible hazards. Additionally – existing GI class is designated, thus allowing the user to estimate current situation of GI in region under the study.
Demo steps:
- Open classification Tool (Viva Grass Planner >> Classification)
- You can create a new classification rule by pressing “New classification” button or use and existing saved rule if you have one by selecting it from the “Select existing classification:” panel and pressing “Open”.
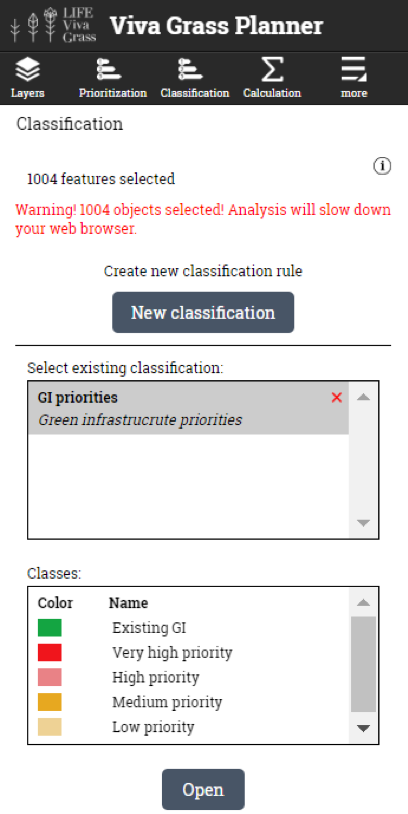
- Opening classification. In this example we use the existing rule.

- Editing or creating classes. You can edit the existing or create new classes within the rule. This is done by manually writing the expression and validating it by pressing the “Test” button.

- Classification result appears in map layer list
 Classification rules (stored in classification rule “Green infrastructure potential”):
Classification rules (stored in classification rule “Green infrastructure potential”):
| Class name | Expression | Comment |
| Existing GI | (natcat = ‘sn’ OR natcat = ‘p’) AND ua1 > 0 | Semi-natural and permanent grasslands near the rivers (first agricultural land from the river bank). |
| VERY HIGH priority | (natcat = ‘arb’ OR natcat = ‘c’) AND ua2 > 0 AND soilfcat = ‘organic’ | Arable land and cultivated grasslands, near rivers.
VERY HIGH priority –organic soils AND in inside flood risk zone; |
| HIGH priority | (natcat = ‘arb’ OR natcat = ‘c’) AND ua2 > 0
|
Arable land and cultivated grasslands, near rivers.
HIGH priority – in flood risk zone |
| MEDIUM priority | (natcat = ‘arb’ OR natcat = ‘c’) AND ua1 > 0 AND soilfcat = ‘organic’ | Arable land and cultivated grasslands, near rivers.
MEDIUM priority – near the rivers (25-50m) AND on organic soils. |
| LOW priority | (natcat = ‘arb’ OR natcat = ‘c’) AND ua1 > 0
|
arable land and cultivated grasslands, near rivers
LOW priority – near the rivers (25-50m) |