 Trade-offs of ecosystem services (aggregated data)
Trade-offs of ecosystem services (aggregated data)
How was it created?
Create mean of ES tradeoff value, convert to raster using created field as value field, run zonal statistics as table on 5km grid. Create 5 categories of values of grid cells to using “natural brakes (jenks)”
What is shown by the layer?

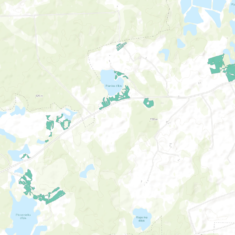
Aggregated data of trade-offs of ecosystem services in “Viva Grass Viewer”
Level of belonging of agroecosystems in 5 km grid cell to certain tradeoff category
Attributes
Tradeoff value in 5x5km grid.
How can it be used?
Overview of spatial distribution of tradeoffs
Update frequency
Same as base map data (Every year)
Explore the data (aggregated data from 2017)
If you want to get the raw data file, request it pressing the button bellow.
Request raw dataTrade-off in benefit of production
Interactions between ecosystem services occur as interactions between bundles. Tradeoff is the situation when values of ecosystem services in one bundle negatively impact values of ecosystem services in other bundle. “Tradeoff in benefit of production” represent the fields where high values in “Production” bundle occur simultaneously with low values in “Habitats” bundle. A clear example in the context of grasslands is the tradeoff between biomass production and biodiversity & habitats: increasing productivity of a grassland usually requires a certain degree of intensification through fertilization, ploughing and reseeding with a mix of selected species. These intensification practices in turn simplify grasslands’ structure and decrease the number of grassland species, leading to a loss of habitats for birds and arthropods.
Trade-off in benefit of habitats
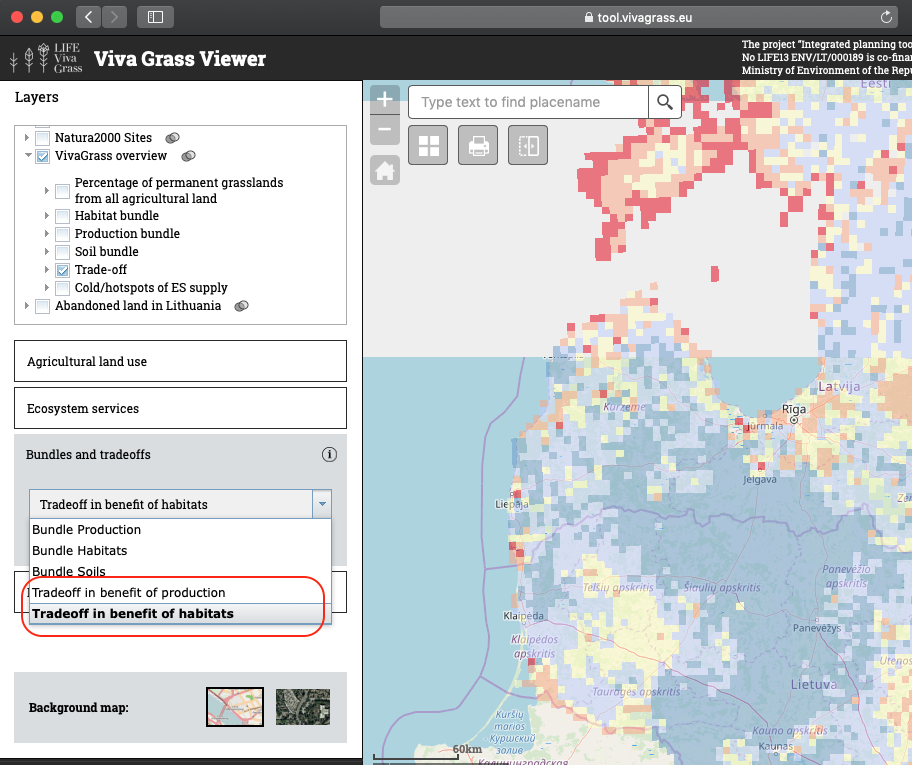
Tradeoffs in “Viva Grass Viewer”
Interactions between ecosystem services occur as interactions between bundles. Tradeoff is the situation when values of ecosystem services in one bundle negatively impact values of ecosystem services in other bundle. “Tradeoff in benefit of habitats” represent the fields where high values in “Habitats” bundle occur simultaneously with low values in “Production” bundle. A clear example in the context of grasslands is the tradeoff between biomass production and biodiversity & habitats: increasing productivity of a grassland usually requires a certain degree of intensification through fertilization, ploughing and reseeding with a mix of selected species. These intensification practices in turn simplify grasslands’ structure and decrease the number of grassland species, leading to a loss of habitats for birds and arthropods.
Explore the data (data from 2017)If you want to get the raw data file, request it pressing the button bellow.
Request raw data