Different grasslands that serve different benefits for people.
The management choices made by humans impact the types, magnitude, and the relative mix of services provided by ecosystems. These are called ecosystem service trade-offs, which accrue when provision of one ecosystem service is reduced because of increased use of another service.
Also the grassland management practices are determining the relative mix of different ecosystem services:
Cultivate grasslands provide the highest yields of the fodder for feeding of the animals as well as the amount of the milk and meat products, but the range of other ecosystem services is much lower compared to permanent and semi-natural grasslands. For example, cultivated grasslands provide considerably less herbs for medicine and cosmetics, unless particular species are specially cultivated. Also the supply of several regulating services is lower – such grasslands are less suitable as habitats for the species of high conservation value as well as for insects, which are providing pollination service. Cultivated grasslands have much lower carbon sequestration capacity, which is important service for regulation of global climate.
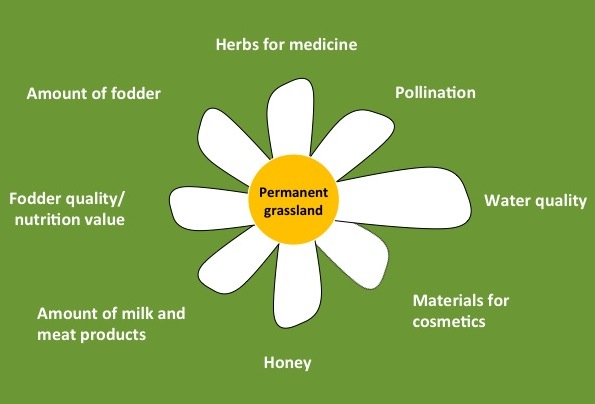
Permanent grasslands provide larger variety of ecosystem service, although the level of fodder production and amount of milk and meat products might be reduced compering to cultivated grasslands. Permanent grasslands usually have higher species diversity, thus providing higher supply with herbs for medicine, materials for cosmetics and honey. Denser sward of the permanent grasslands support erosion control on steep slopes as well as increase the nutrient absorption capacity and thus improving the water purification service. Permanent grasslands have also much higher carbon sequestration capacity.
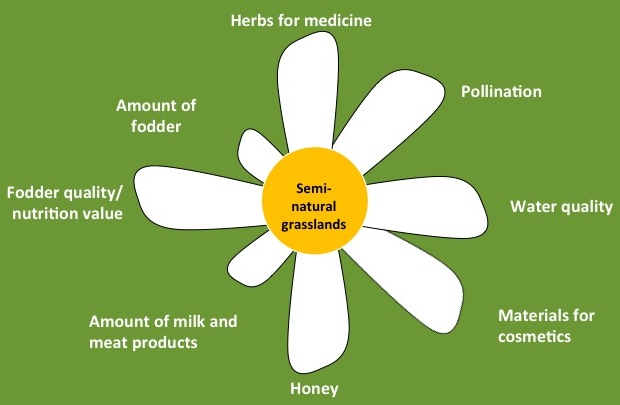
Semi-natural grasslands have the highest species diversity, which has also positive impact on range of provisioning services, e.g. quality and nutrition value of fodder, because of higher variety of micro-element, supply of honey, herbs for medicine and materials for cosmetics. Furthermore, in addition to the regulating services provided by other permanent grasslands, the semi-natural grasslands have higher contribution to maintenance of habitats for engendered species and pollinators. Semi-natural grasslands can supply higher rates of cultural services, including the recreational, education, scientific, aesthetic and cultural heritage value.
| Cultivated grasslands | Permanent grasslands | Semi-natural grasslands |
 |
 |
 |
Moreover the magnitude of the ecosystem services can be also influenced by the abiotic properties of the ecosystem, such as soil fertility, moisture and relief. For example, grasslands with higher soil fertility provides higher yields of fodder as well as higher capacity of nutrient absorption in soil, whereas grasslands with low soil fertility usually are more species rich, thus providing more herbs for medicine and habitats for species. Grasslands on steep slopes are more valuable with regard to providing service of erosion control comparing to grasslands on plains and usually have higher aesthetic value and tourism potential.






No comments yet.